Satyajit says that the Christmas tree and Gita’s Pipal tree are symbols of death, rebirth, and immortality across cultures. An exclusive for Different Truths.
PLANET’S PLANTS LIKE PINE AND PIPPLA TREES POINT TO PENULTIMATE PURUSHA AND PARAMA PURUSHA
Globally, December–January is the time for festive celebrations on two special spiritual aspects: Christmas and Gita Jayanti.
Surprisingly, both celebrations point to presenting their relevant trees. The Christmas tree and Gita’s Pipal tree symbolise death, resurrection, and immortality. The Christmas tree symbolises the birth and resurrection of Jesus Christ. The tree’s branches and shrubs are viewed as an emblem of immortality and are said to be symbolic—the crown of thrones worn by Christ on the cross. The Christmas trees are usually pine or fir trees. Herewith, it is evident that there’s enough and ample scope for further analogical detection and elaboration about the said pine tree and pipal tree, regarding their spiritual, philosophical, and social deliberation.
Now, let’s see the role of the pipal tree in the context of Gita in symbolising death, resurrection, and immortality.
ऊर्ध्वमूलमधःशाखमश्वत्थं प्राहुपव्ययम्।
छन्दांसि यस्य पर्णानि यस्तं वेद स वेदवित्।। (1/15)
“He who knows the Asvattha / Pipal tree (in the form of Creation), which is said to be imperishable with its roots in the Primeval Being (God), whose branch is represented by Brahma (the Creator), and whose leaves are the Vedas, is a knower of the purport of the
Vedas.”
This is the first hymn of Purushottoma Yoga. Purushottma Yoga is the 15th chapter of the Sreemad Bhagavad Gita. It portrays immense philosophical and spiritual significance, importance, and application.
Whenever there’s a Pravachana or discourse on the Gita, irrespective of chapters, Purushottma Yoga automatically comes in as a reference. A reference comes in, explaining the core and fundamentals of the Gita.
From a practical application point of view, these twenty slokas of Purushottoma Yoga were offered as mantras in the process of the Havan, an oblation ceremony. These twenty mantras are dedicated 108 times as Aahuti or offerings. Again, as a rule of ritual, ashramites, sadhus, and sanyasis of different Ashrams, Matts, or Akharas, cite these twenty slokas before taking their mid-day meals. Also, in all usual Sadhu-Bhandara, which is, when a congregation of invitee sadhu-sanyasis are offered a meal, their chorus chanting of the slokas of Purushottma Yoga presents an air of century-old atmosphere of a spectacular sequence of prayers on offering the meal to God. Therefore, Purushottma Yoga has special importance and treatment.
One of the main essences of the Gita that is expressed through this Purushottma Yoga is the division of Purusha. That is, destructible, indestructible, and Purushottom, or the Parama Purusha.
Now the first sloka, given above in Sanskrit, depicts the pipal tree as a symbol of universal manifestation. Those who mastered the wisdom of the Veda (commonly known as Vedaveed), have explained that the universal livelihood, or global sansar, is as if a pipal tree. Its roots are projected upward, and its branches are shown downward. This pipal tree is as if indestructible.
Unseen is Brahma as the invisible upward root, who beholds and maintains this physical and behavioural Sansar of beings.
But why do the roots shown go upward? Tree roots are always seen going down into the earth to collect extracts for their livelihood. Here, in the sloka, the root of the Asavtta, or the pipal tree, is shown to be going upward because of its spiritual and philosophical deliberations. For the supreme source of knowledge for the ultimate origin of creation, we receive it from that all-pervading, unseen Brahma. Again, doctrinally, the Lokas, or plains of creation, are categorised into seven stages, i.e., Bhuh, Bhubhah, Swah, Mahah, Janah, Tapah, and Satya. This Satya Loka is the highest plain or, the origin of creation and thus, the seat of Brahma. So why are the roots shown going upwards?
‘Adhah Sakham’—branches are shown downward. That is the wishes and desires of beings spread in all directions but usually remain in the behavioural common craving for belongings and don’t go upward for seeking Brahma Loka.
Leaves are like Vedas. That is, trees suck vital extracts from the soil, and that extract is mixed with vitamins. Vitamins: a tree collects them from sun rays through its leaves. In this rhythmic process, a tree gets and maintains its life force. The fruits of Dharma-Adharma (good and evil) serve to keep the universal Sansar running in a similar way that we as beings sustain happiness in our livelihood and life force. Again, under oblation rituals, beings receive developments and an enhanced life force because the Vedas direct the ritual process, known as Karmakanda. This wheel of Karmakanda never allows beings to attain renunciation but to remain in a rotational livelihood.
Universal livelihood is like the symbolic Asavtta tree, which is always changing and has no permanence. Dharma and Adharma are like two fruits of pleasure and pain. Whoever knows this tattva is a true Vedabeed.
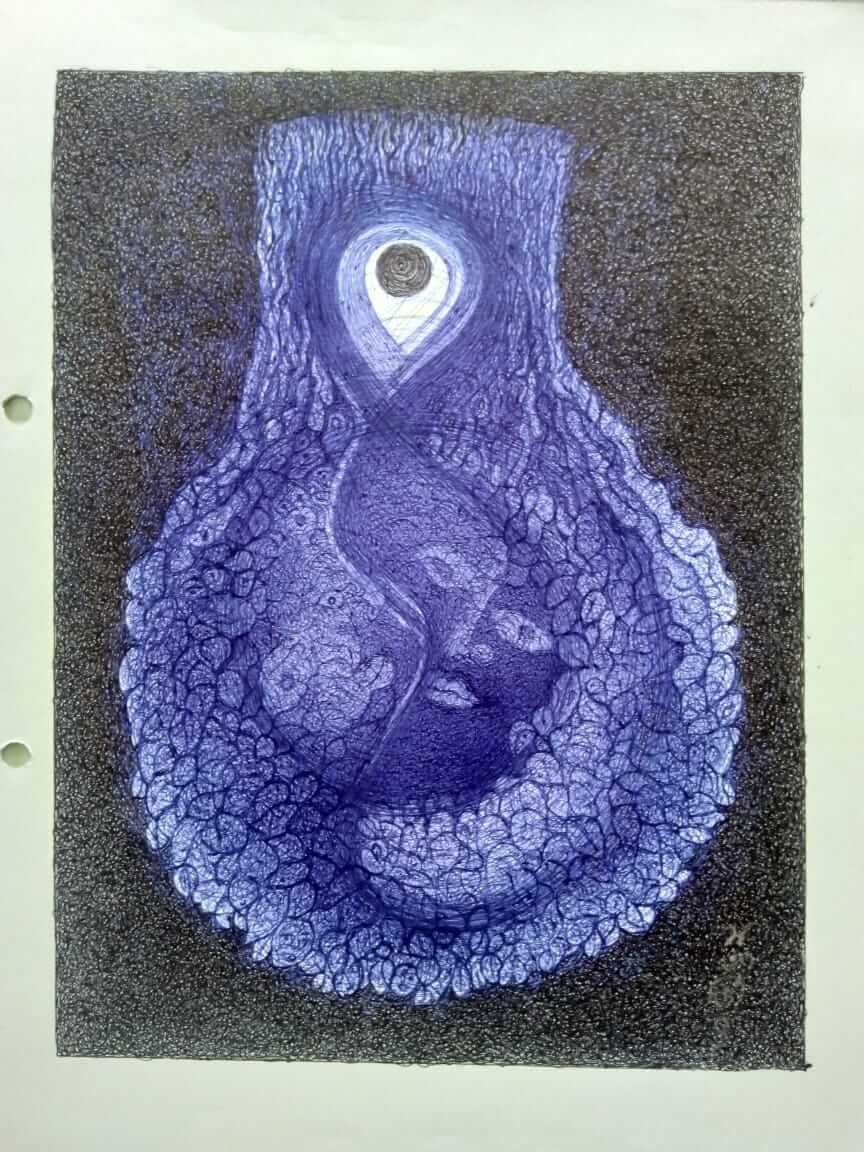
Given above, the drawing (pen and ink) of the sloka is a representation of Sree Vidya Art, a spiritual process of application of Passivity and Renunciation.
Interestingly, we, as common people, may not be so aware of this symbolic Pipal tree for its philosophical wisdom, but there are always some who know the value of the symbol.
The pendant of a necklace shows below how nicely fashion-designing experts have taken up the philosophy of “urdha mula.”
Painting by the author




 By
By

 By
By
 By
By