Ebola is a deadly disease caused by a virus. The virus is rare but wreaks havoc on the human body but one can catch it only by coming in direct contact with an infected person’s body fluids. Earlier, it was called as Ebola haemorrhagic fever. Dr. Preeti tells us more about it, exclusively for Different Truths.
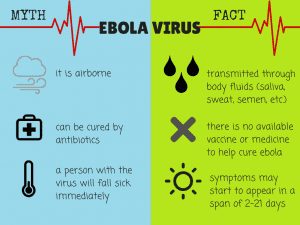
Ebola is a deadly disease caused by a virus. It has five strains and four are deadly. After entering the body, the virus kills the human cells, making some of them to explode, which wrecks the human immune system, causing heavy internal bleeding and damaging all organs. The virus is rare but wreaks havoc on the human body but one can catch it only by coming in direct contact with an infected person’s body fluids. Earlier, it was called as Ebola haemorrhagic fever. It is transmitted from wild animals in the human population. If untreated it is fatal. It first appeared in 1976 in Africa and again in 2014-2016 in West Africa. It was deadlier than the first outbreak of 1976.
Transmission
It was thought that fruit bats are natural Ebola virus hosts. Ebola is introduced into the human population through close contact with blood, secretions, fluids of infected animals like chimps, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, porcupines found in the rainforests. Thereafter, Ebola then spreads through human to human transmission via direct contact with broken skin, fluids, blood, etc. Burial ceremonies involving direct contact with the body of the deceased can also transmit the virus.
Symptoms
The common symptoms of this disease are fever, sore throat, body aches, diarrhoea, headache, muscle pain, chills and later person may experience internal bleeding resulting in vomiting or coughing of blood, fatigue and stomach pain. Symptoms take 2—21 days for onset after exposure to Ebola. For patients who survive infection may remain contagious for 21-42 days after which symptoms abate.
Treatment
It is treated by supportive therapy i.e., balancing the patient’s fluid and electrolytes maintaining their oxygen status and blood pressure. Patients are isolated and caregivers wear protective garments.
Complications of Ebola Fever
It has many complications like organ failure, jaundice, delirium, shock, seizures, coma, and death. People who survive take months to recuperate and experience fatigue, headaches, hair loss, hepatitis, and in males the virus lingers for six months in the semen.
Prevention of Ebola
The main way to prevent Ebola is not to travel to endemic places. In December 2016 clinical trial of rVSV-ZEBOV Vaccine was apparently safe for Ebola disease.
Health care workers need to use health hygiene and protective garments.
Men should refrain from sexual activity for several months after infection.
If by chance one visits an Ebola endemic area, one should avoid eating raw meat of ape, bat, and monkey.
People should not have contact with blood, meat, body fluids of animals showing the disease.
Interesting Facts about Ebola Virus
- It is not waterborne or airborne
- Without proper cleaning and sterilization of medical equipment Ebola spreads quickly.
- The virus is a severe, acute, viral disease often mistaken as malaria, typhoid, cholera, plague, leptospirosis, shigellosis and relapsing fever.
- Symptoms occur rapidly
- Ebola can be diagnosed by ELISA, antigen detection test, serum neutralisation test, electron microscopy.
- It was first discovered in 1976 in former Zaire near the Ebola river, so the name comes.
- It has only been around for 40 years
- Scientists have found 4 out of the 5 species of the virus are found in animal hosts which are natives of Africa.
- People recovering from Ebola develop antibodies which last for 10 years.
- It can reproduce in eight hours.
- Experimental drugs are being developed like ZMapp which is produced in genetically modified tobacco plants.
- The fifth virus strain Reston virus is non-pathogenic to humans.
©Dr. Preeti Talwar
Photos from the Internet
#EbolaVirus #Virus #KillingVirus #FactsAboutEbolaVirua #HowToPreventEbola #EbolaTreatment #EbolaSymptoms #Medicine #Disease #Africa #DifferentTruths







 By
By